Uniaxial Geogrid vs Biaxial Geogrid, what is The Difference?
Geogrids are geosynthetics that have become an integral part of a wide range of construction projects, from roads to retaining walls. These materials play a key role in improving the stability and performance of structures such as roads, retaining walls and slope stabilization, providing stability and strength that natural soils cannot achieve. So what is the difference between unidirectional and bidirectional geogrids? When choosing to use unidirectional or bidirectional geogrids, how should you weigh the pros and cons and make the best choice?
This depends on the comprehensive consideration of many factors such as the requirements of the specific project, the load distribution characteristics and the intended application. Only by choosing the most appropriate geogrid solution can the stability, performance and durability of the entire system be ensured.
1. What are The Key Structural Differences Between Uniaxial and Biaxial Geogrids?
The key structural differences between uniaxial and biaxial geogrids lie in their unique directional properties:
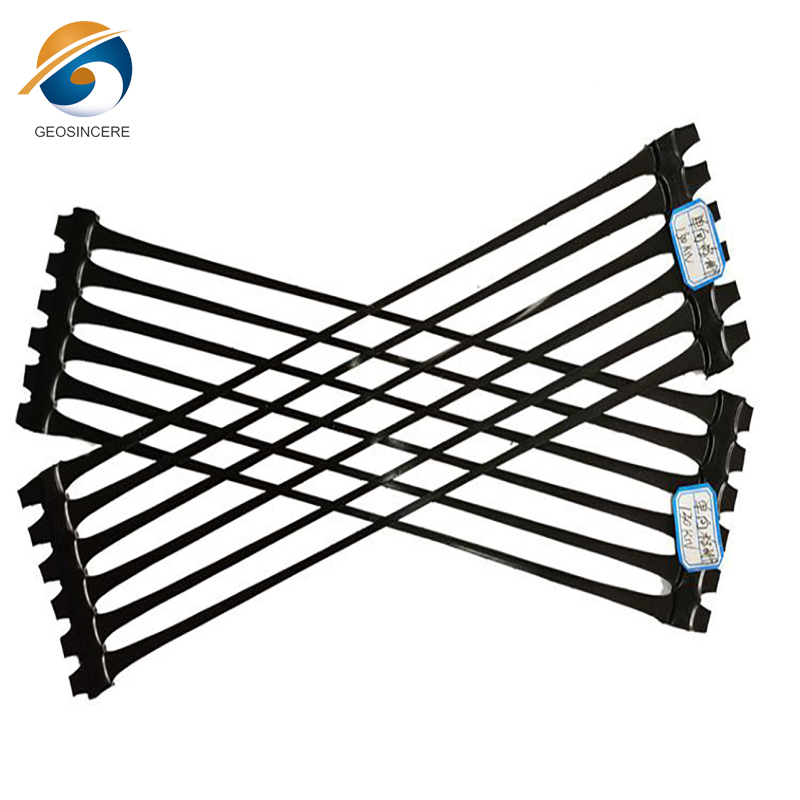
1.1 Uniaxial Geogrids:
- Uniaxial geogrids are designed with a primary direction of strength, typically running in a single axis.
- This unidirectional orientation allows for enhanced reinforcement along a specific direction, making them well-suited for applications where the stress is concentrated in one predominant orientation, such as in slope stabilization or retaining wall construction.
- The ribs and apertures (open spaces) of a uniaxial geogrid are aligned in a singular direction, enabling efficient load transfer and soil interaction along that axis.
1.2 Biaxial Geogrids:
- Biaxial geogrids, possess strength and stiffness in two orthogonal (perpendicular) directions.
- This balanced, multi-directional reinforcement makes biaxial geogrids versatile for applications where stress and strain may occur in multiple orientations, such as in unpaved road construction or soil stabilization projects.
- The intersecting ribs and apertures of a biaxial geogrid create a grid-like structure, providing reinforcement in both the longitudinal and transverse directions.
The choice between uniaxial and biaxial geogrids ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the project and the anticipated loading conditions. Uniaxial geogrids excel in situations where the stress is predominantly unidirectional, while biaxial geogrids offer a more comprehensive solution for multidirectional reinforcement needs.
2. How Do The Reinforcement Properties of Uniaxial and Biaxial Geogrids Compare in Various Applications?
The reinforcement properties of uniaxial and biaxial geogrids can vary significantly, depending on the specific application and the desired performance criteria. Let's explore how these two types of geogrids compare in different construction scenarios:
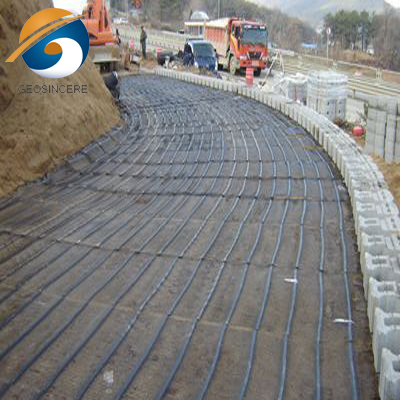
2.1 Slope Stabilization and Retaining Walls:
- Uniaxial geogrids excel in slope stabilization and retaining wall applications, as they provide robust reinforcement along the primary direction of the slope or wall, effectively resisting tensile forces.
- Biaxial geogrids can also be used in these applications, but their balanced reinforcement may not be as efficient as the targeted reinforcement provided by uniaxial geogrids.
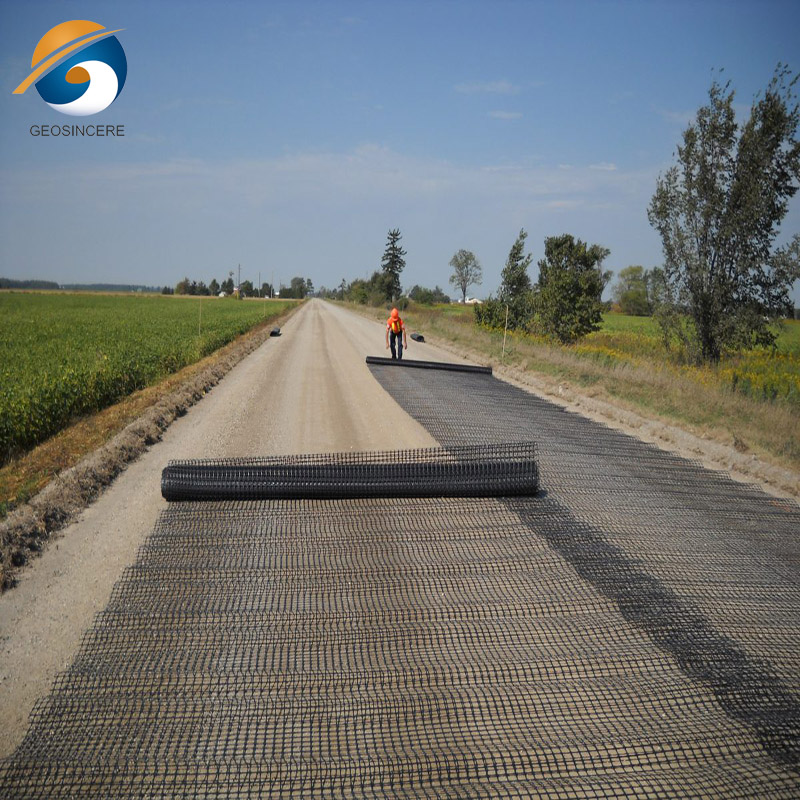
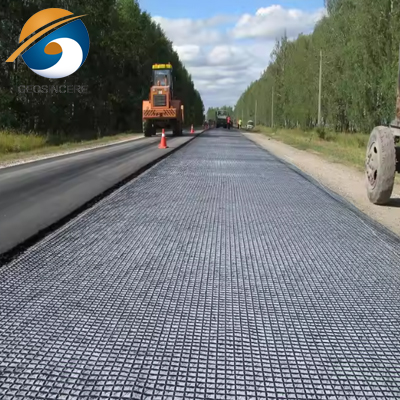
2.2 Unpaved Road Construction:
- Biaxial geogrids are the preferred choice for unpaved road construction, as they offer reinforcement in both the longitudinal and transverse directions.
- This multidirectional reinforcement helps distribute the loads more evenly, preventing rutting and improving the overall stability of the road structure.
- Uniaxial geogrids may not be as effective in this application, as they lack the reinforcement in the secondary direction.
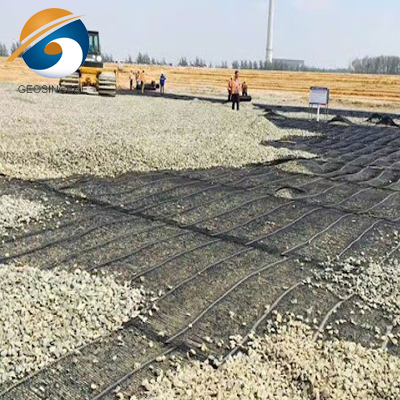
2.3 Soil Stabilization:
- For soil stabilization projects, such as working platforms or load-bearing foundations, biaxial geogrids are generally more versatile.
- The balanced reinforcement of biaxial geogrids helps to confine and reinforce the soil in multiple directions, enhancing the overall bearing capacity and reducing the risk of differential settlements.
- Uniaxial geogrids can still be used in certain soil stabilization applications, but their effectiveness may be limited to the primary direction of reinforcement.
2.4 Embankment Construction:
- Both uniaxial and biaxial geogrids can be used in embankment construction, but their specific roles may differ.
- Uniaxial geogrids are often employed to provide tensile reinforcement along the embankment face, helping to maintain slope stability.
- Biaxial geogrids can be utilized within the embankment body, offering multidirectional reinforcement to enhance the overall stability and load-bearing capacity.
3. What are The Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Uniaxial and Biaxial Geogrids for a Particular Project?
3.1 Stress and Strain Directivity:
- Evaluate the predominant directions of stress and strain in the application.
- If stress is primarily unidirectional, a uniaxial geogrid may be more appropriate because it can provide targeted reinforcement along the critical axis.
- For applications with multi-directional stresses and strains, biaxial geogrids can provide a more comprehensive reinforcement solution.
3.2 Soil Conditions and Interactions:
- Consider the properties of the soil, including its shear strength, bearing capacity, and deformation sensitivity.
- Uniaxial geogrids may be more appropriate for soil conditions that require reinforcement to be concentrated in a specific direction, such as in slope stabilization.
- Biaxial geogrids are more effective in soils that require a more balanced load distribution, such as in unpaved road construction or in soft foundation soils.
3.3 Project Requirements and Performance Goals:
- Clearly define project requirements, including expected service life, bearing capacity, and overall stability needs.
- If the project requires a higher degree of tensile reinforcement in a specific direction, uniaxial geogrids may be the preferred choice.
- For applications that require more comprehensive reinforcement and load distribution, biaxial geogrids may be a better choice.
3.4 Constructionability and Installation:
- Evaluate the ease of installation and compatibility with the project construction techniques.
- Uniaxial geogrids may be easier to install in certain applications because they are more straightforward in orientation.
- Biaxial geogrids may require more careful placement and overlap to ensure the desired reinforcement is achieved in both directions.
By carefully considering these key factors, an informed decision can be made as to whether uniaxial or biaxial geogrids are the most appropriate solution for a particular project, thereby optimizing the performance and cost-effectiveness of the overall design.
4. Common use cases where uniaxial or biaxial geogrids are preferred for an application.
4.1 Uniaxial geogrids:
- Reinforcement of earth walls: Uniaxial geogrids are ideal for reinforcing earth walls as their primary tensile strength is perpendicular to the wall, providing strong lateral support.
- Slope stabilization: On steep slopes, uniaxial geogrids can be used to reinforce the soil and prevent slippage, with high-strength ribs running parallel to the slope.
- Embankment construction: When building embankments on soft or weak soils, uniaxial geogrids can be used to increase bearing capacity and prevent excessive settlement.
- Railway ballast reinforcement: In railway applications, uniaxial geogrids are often used to reinforce ballasts where the primary forces are longitudinal.
4.2 Biaxial geogrids:
- Paved roads and parking lots: Biaxial geogrids offer excellent reinforcement in both the longitudinal and transverse directions, making them ideal for road, parking lot and other paved surface construction.
- Reinforced Earth Walls: Biaxial geogrids can be used in the construction of reinforced earth walls, where their grid-like structure better distributes stresses in multiple directions.
- Load-bearing Platforms: In applications where the load distribution is more complex, such as load-bearing platforms or working platforms, biaxial geogrids can effectively distribute loads and prevent excessive settlement.
- Embankments on Soft Soils: Biaxial geogrids can be used to reinforce embankments built on soft or compressible soils, providing stability in both the longitudinal and lateral directions.
The choice between uniaxial and biaxial geogrids ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the project, the nature of the loads, and the performance characteristics required of the entire system.
5. Summarize
Geogrids have become an indispensable component in a wide range of construction projects, from roads to retaining walls, playing a crucial role in enhancing the stability and performance of these structures. The choice between unidirectional (uniaxial) and bidirectional (biaxial) geogrids involves a careful consideration of various factors to determine the most suitable solution.
By selecting the most appropriate geogrid solution, the stability, performance, and durability of the entire system can be ensured, optimizing the long-term performance and cost-effectiveness of the construction project.