Can Geomembranes Solve the Challenges of Waste Management?
In recent years, waste management has emerged as a critical global challenge, with growing concerns about environmental pollution and resource depletion.In the face of mounting waste management challenges, the need for effective and sustainable solutions has never been more critical.However, innovative solutions such as geomembranes have shown significant promise in addressing these challenges. Geomembranes, impermeable synthetic membranes used for containment and barrier systems, offer multiple advantages that including containment, barrier protection, and environmental preservation. In this article, we will explore how geomembranes can revolutionize waste management practices and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
1. What is Geomembrane?
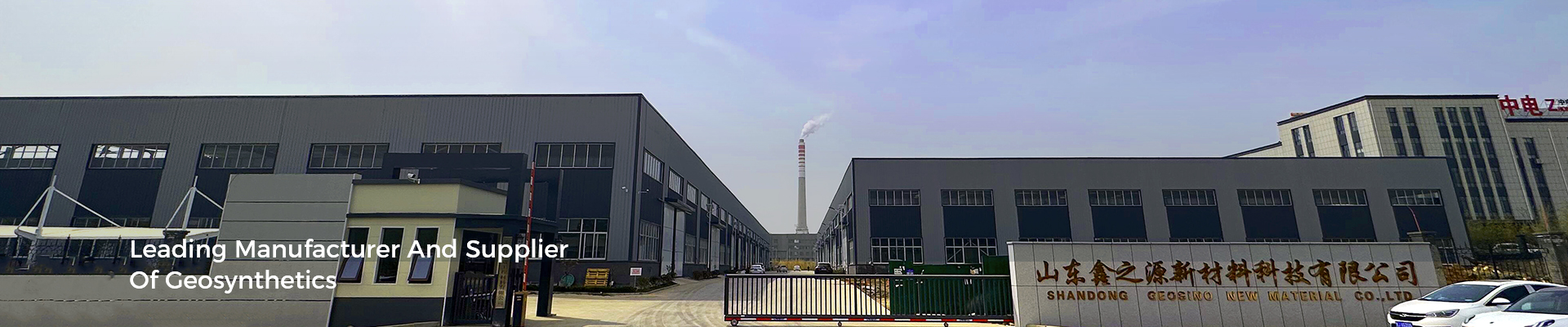
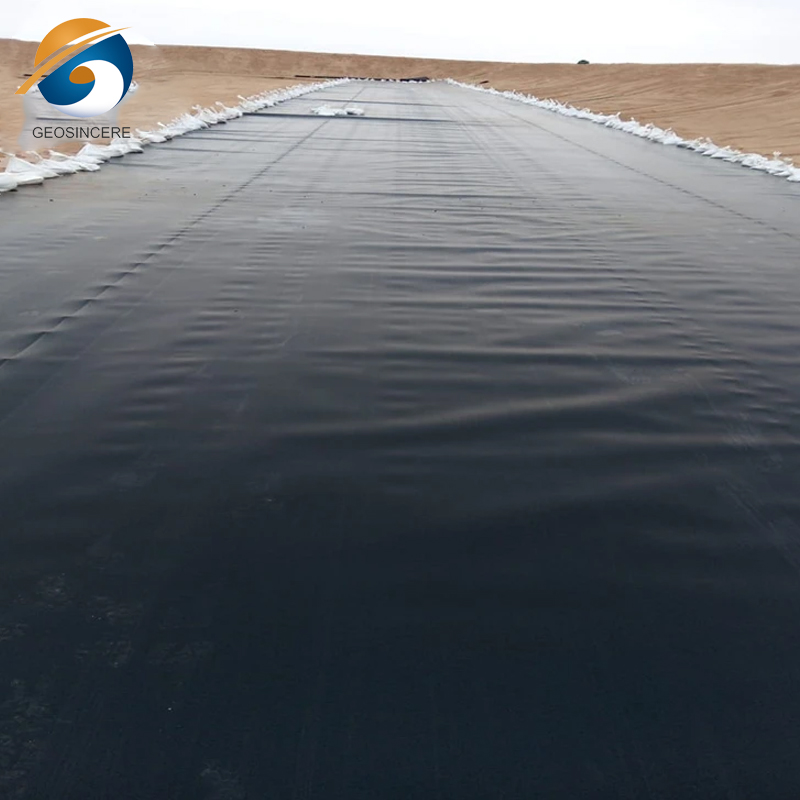
A geomembrane is a synthetic material used as a barrier in various applications, particularly in waste management and environmental protection.Geomembranes are usually made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) materials.HDPE is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent durability, strength, and chemical resistance.
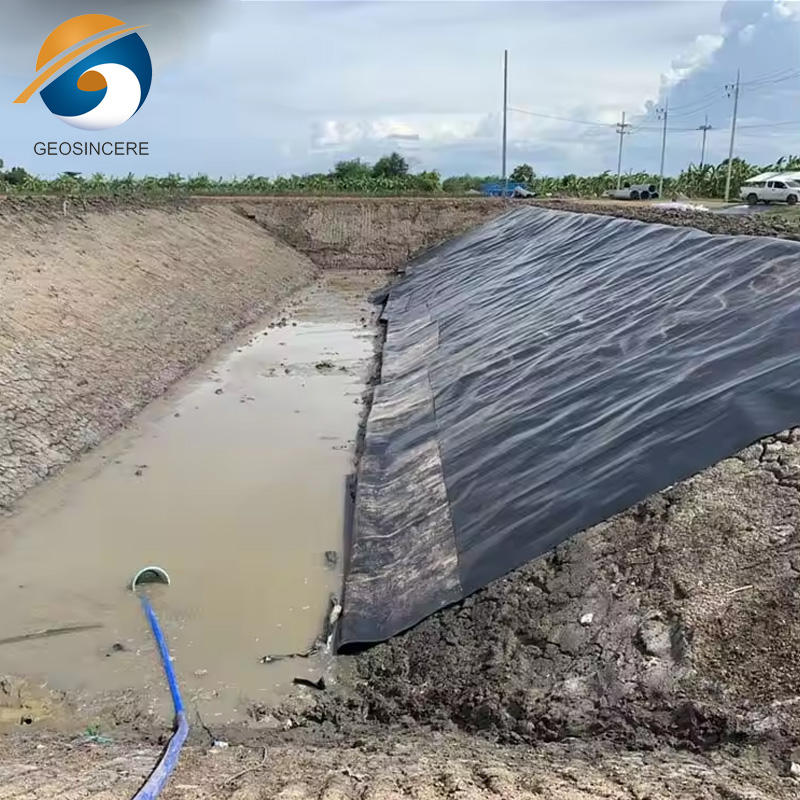
Geomembranes are designed to have low permeability, meaning they are resistant to the passage of gases, liquids, and contaminants. They are used to prevent the migration of pollutants, such as leachate, from waste disposal sites into the surrounding soil and groundwater. Geomembranes are also employed in other applications, including mining, agriculture, and water containment, Their high tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to UV radiation make them suitable for diverse environmental conditions and demanding applications.
2. Environmental Protection
In the realm of waste management, a pressing global issue, the utilization of geomembranes has emerged as a promising solution. Geomembranes, synthetic materials engineered to act as impermeable barriers, offer a range of benefits that can address the challenges faced in waste management practices. Including landfills, hazardous waste storage sites, and wastewater treatment plants.By isolating these waste materials within designated areas, geomembranes prevent their migration and minimize the potential for environmental contamination ,Ensuring the protection of both human health and the environment.
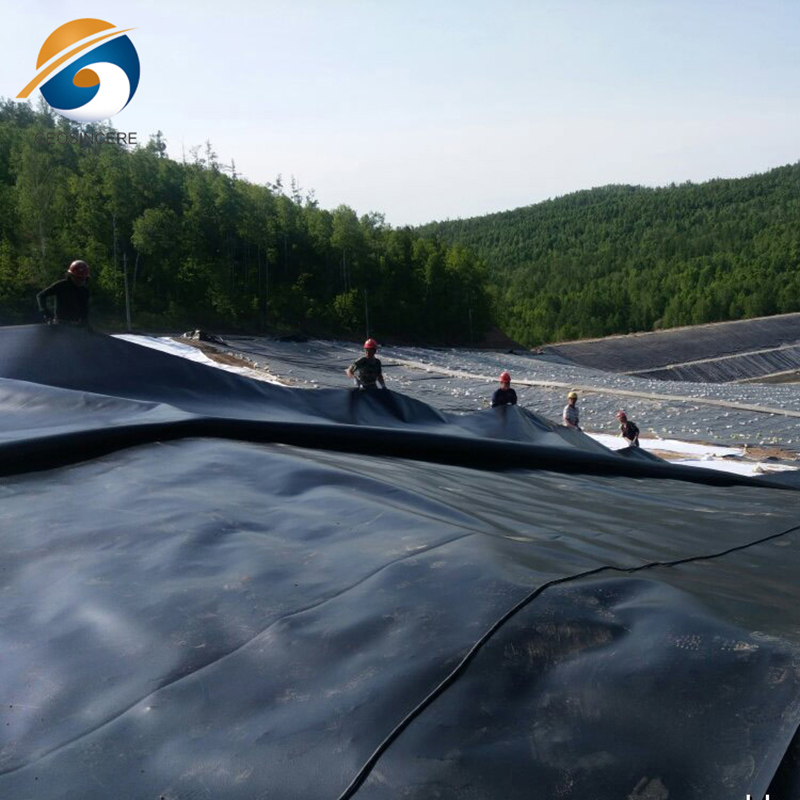
2.1 Landfill Management
Waste management has become a pressing global issue due to the exponential growth of waste generation and the limited capacity of traditional disposal methods. Landfills, in particular, pose significant environmental risks, such as soil and groundwater contamination, greenhouse gas emissions, and aesthetic degradation.
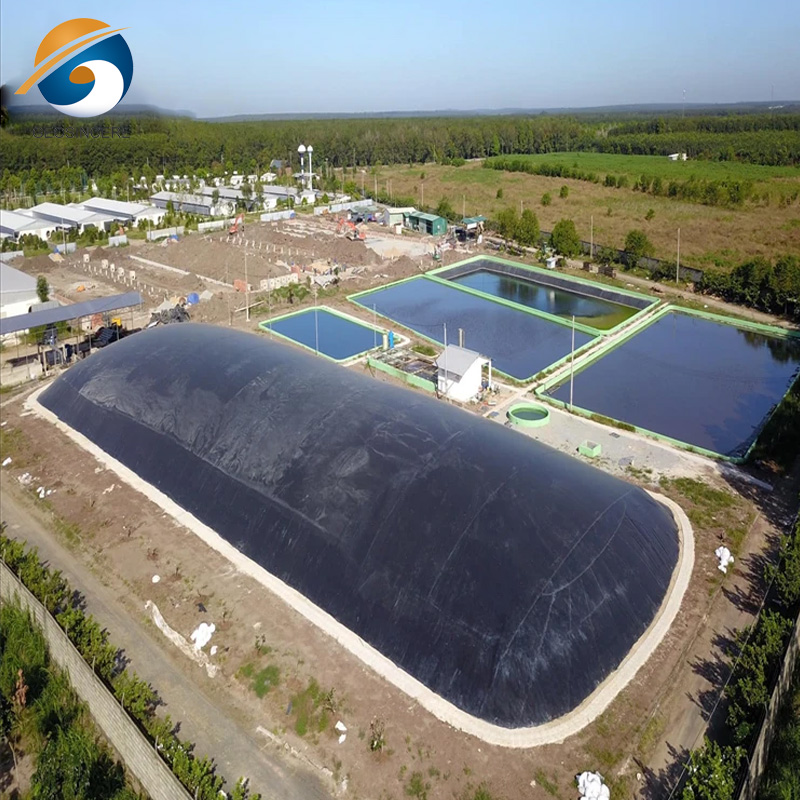
Geomembrane landfills often produce landfill gas, primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide. Proper gas management systems, including gas collection wells, gas extraction systems, and gas monitoring, are implemented to prevent gas buildup, mitigate odors, and reduce the risk of explosions or fires.
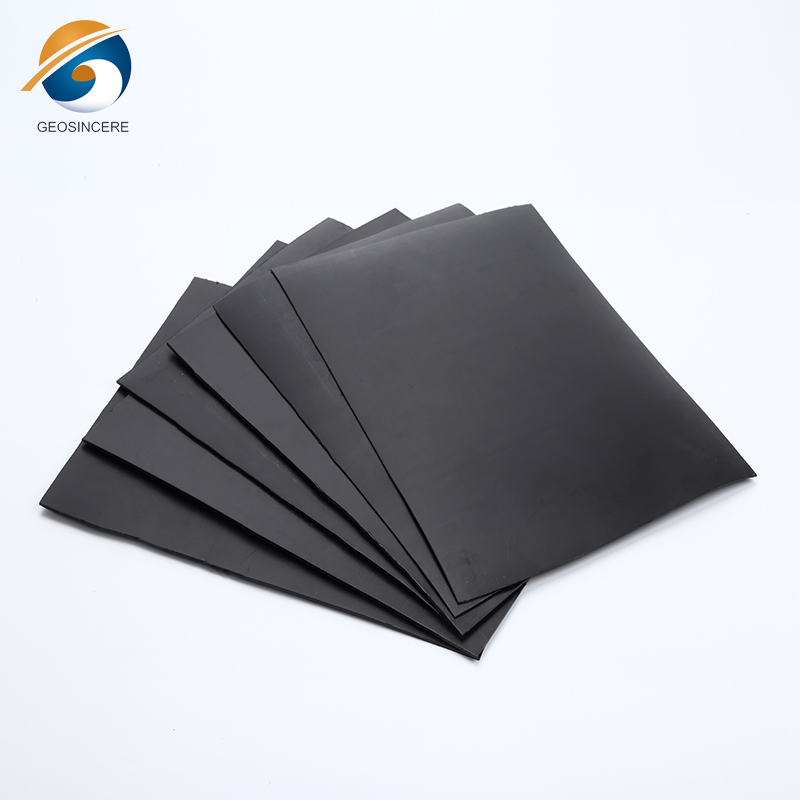
Geomembranes offer a viable alternative by providing an impermeable barrier that prevents leachate and contaminants from seeping into the surrounding environment.This containment capability is crucial in safeguarding ecosystems and protecting public health, as it reduces the risk of contamination and the potential negative impacts on both the environment and human populations.
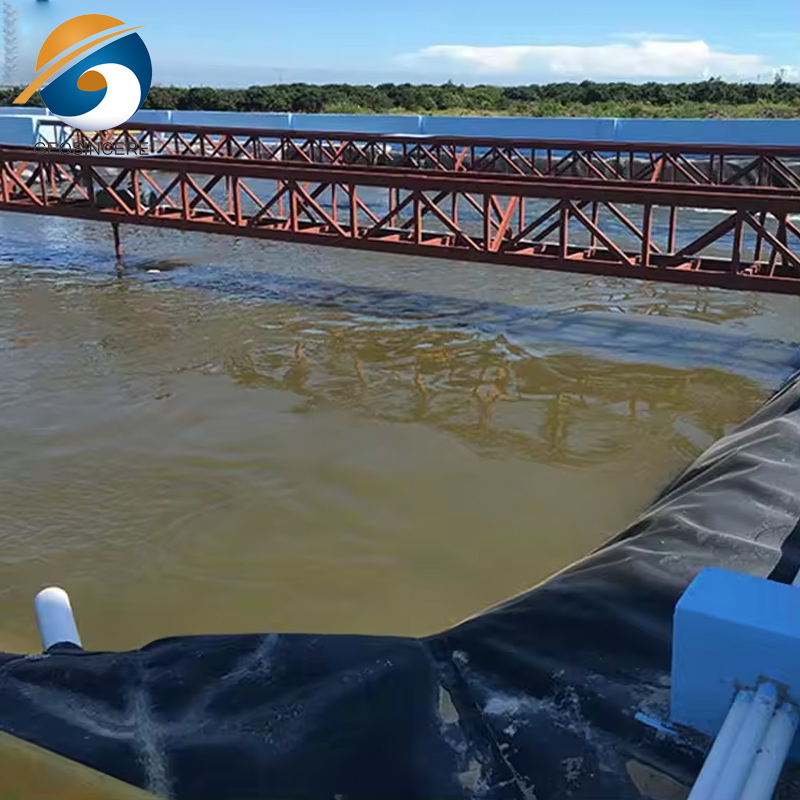
2.2 Wastewater Treatment
In wastewater treatment facilities, geomembranes find application in the construction of anaerobic digestion tanks, sedimentation basins, and lagoons. By creating impermeable barriers, they facilitate the effective separation and treatment of wastewater components such as sludge and effluents. This containment and control of wastewater prevent its release into natural water bodies, thus safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and public health.
One of the key advantages of geomembranes is their impermeability. They are typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) materials that exhibit excellent resistance to chemical and biological degradation. This resistance ensures that the geomembrane remains intact and maintains its barrier properties even when exposed to harsh wastewater conditions.
Geomembranes are also very flexible and can conform to the shape of the underlying terrain or structure, allowing for seamless installation and minimizing the risk of leakage. They can be customized to meet specific project requirements.
2.3 Control Hazardous Waste
In the context of controlling hazardous waste, geomembranes are primarily used for lining landfills, storage ponds, impoundments, and other containment structures. They are designed to withstand the aggressive nature of hazardous substances, including corrosive chemicals, toxic compounds, and industrial byproducts.These specialized liners provide a reliable barrier to contain and isolate hazardous materials, preventing their release into the environment and minimizing the risk of contamination.
Another advantage of geomembranes is their long service life and minimal maintenance requirements. This reduces the potential for leaks or failures in hazardous waste containment systems over time. They exhibit resistance to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure, ensuring their durability and reliable performance throughout the lifespan of the facility.
Geomembranes play a critical role in controlling hazardous waste by providing a durable, impermeable, and chemically resistant barrier. Their ability to withstand harsh substances, conform to different surfaces, and require minimal maintenance makes them an indispensable component in ensuring the safe containment and management of hazardous waste.
3. Resource Conservation
In addition to their environmental benefits, geomembranes also play a significant role in resource conservation. By effectively containing waste materials, these liners contribute to the preservation of valuable resources that can be recovered through recycling and proper waste management practices. This conservation approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy and promotes sustainable resource utilization.
When hazardous waste is not properly contained, it can seep into the surrounding environment, leading to the contamination of soil, water, and air. This contamination not only poses risks to human health and ecosystems but also results in the loss of valuable resources that could have been recovered and reused.
The use of geomembranes in resource conservation also aligns with the principles of a circular economy. In a circular economy model, resources are kept in use for as long as possible, and waste is minimized through recycling, reusing, and recovering materials. Geomembranes facilitate this approach by preventing the loss and dispersion of waste materials, creating opportunities for resource recovery and promoting sustainable practices.
4. Cost-effectiveness
Geomembranes offer long-term cost savings in waste management. Their durability and resistance to chemical degradation reduce the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.The use of geomembranes contributes to efficient waste management practices, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste generation. By effectively containing waste materials, these liners allow for better control and management of waste streams, enabling the implementation of recycling and recovery strategies. This reduction in waste generation leads to cost savings associated with disposal and landfill fees.
5.Environmental Sustainability
Geomembranes play a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability in waste management practices.Provided a practical and effective solution to address the challenges of waste management.Their ability to protect the environment, manage landfills, contain waste, conserve resources, and deliver cost savings make them a valuable tool in promoting sustainable waste management practices. By embracing geomembranes and integrating them into waste management strategies, societies can make significant strides in achieving efficient and environmentally responsible waste disposal practices.